Online CPR courses have become an accessible way for individuals to learn life-saving skills from the comfort of their homes. Whether you’re a healthcare worker, parent, or someone who wants to be prepared for emergencies, these courses offer essential knowledge. Obtaining CPR certification online ensures you meet recognized standards, equipping you to act confidently when needed. But what exactly will you learn in an online CPR course? In this article, we’ll break down the key skills and techniques you can expect to master.
Introduction to CPR Basics
Online CPR courses start with the basics, ensuring participants understand what CPR is and why it’s critical during emergencies. CPR, or cardiopulmonary resuscitation, involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to keep blood flowing to vital organs. You’ll learn how these actions can make a difference between life and death in cases of sudden cardiac arrest.
Recognizing an Emergency
A crucial part of CPR training is identifying when to act. Courses teach you how to recognize the signs of cardiac arrest, such as a person collapsing, not breathing, or becoming unresponsive. Knowing how to stay calm under pressure and assess the situation is a key skill taught early in the program.
Checking Responsiveness and Calling for Help
In an emergency, every second counts. You’ll learn to check for responsiveness by tapping the person and calling their name. If there’s no response, the course emphasizes contacting emergency services immediately. These initial steps ensure professional help is on the way while you begin CPR.
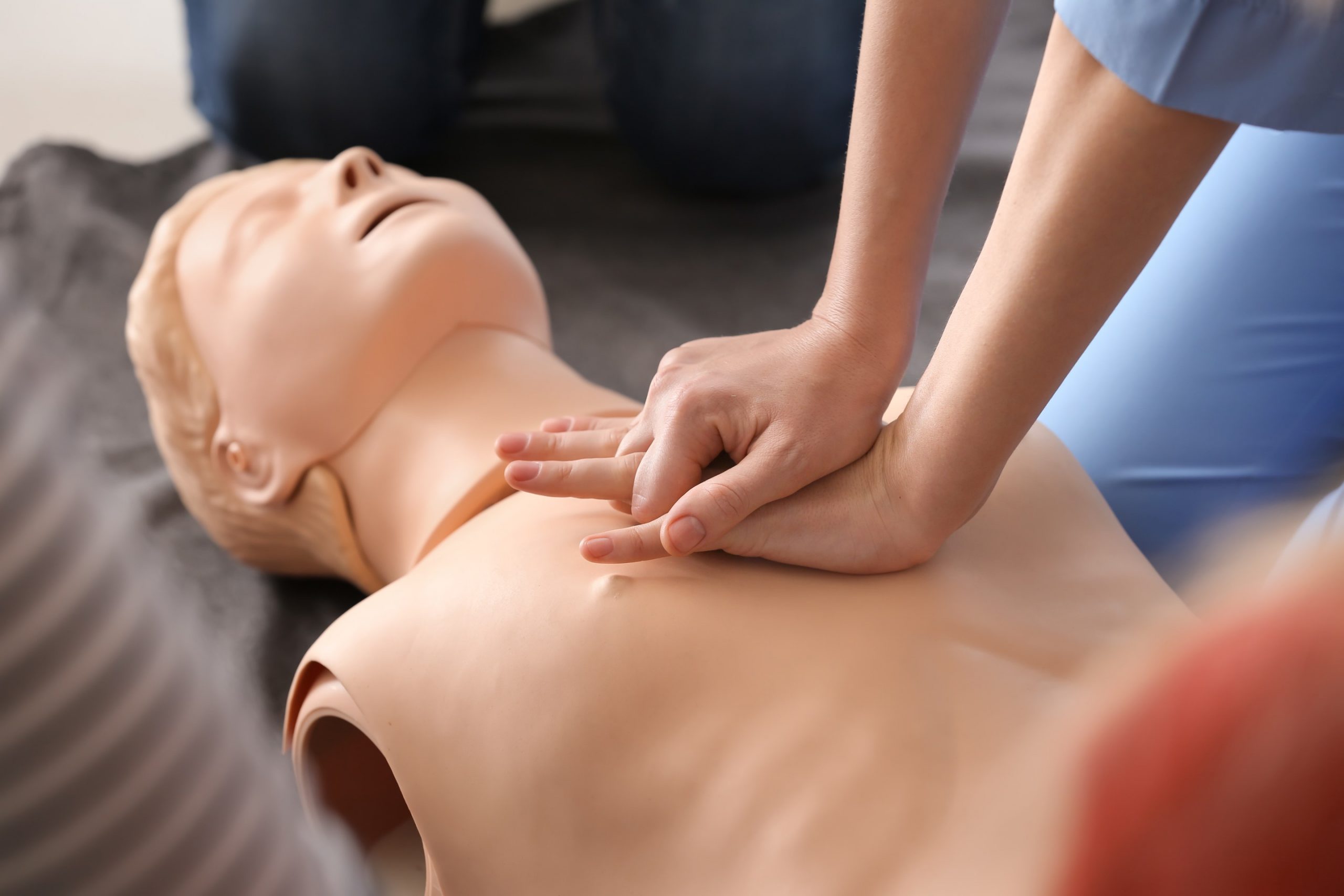
Mastering Chest Compressions
One of the most important skills taught is performing chest compressions correctly. The course explains how to place your hands, the depth of each compression, and the ideal rate (usually 100 to 120 compressions per minute). You’ll also learn how to adjust pressure depending on the victim’s age, whether it’s an adult, child, or infant.
How to Deliver Rescue Breaths
Along with chest compressions, rescue breaths are a vital part of CPR. Online courses demonstrate how to tilt the person’s head back, open the airway, and give effective breaths. You’ll learn the recommended ratio of compressions to breaths (usually 30:2) and what to do if the breaths don’t go through due to airway blockages.
Understanding Hands-Only CPR
Some online courses also cover hands-on CPR, which focuses solely on chest compressions. This method is particularly useful for those uncomfortable with rescue breaths or when immediate breaths are not necessary. Hands-only CPR can still keep blood circulating until professional help arrives.
Using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
Many CPR courses include instructions on using an AED, a portable device designed to restore a regular heart rhythm. You’ll learn how to power the AED, follow its audio prompts, and place the pads on the person’s chest. While AEDs guide you through the process, understanding how to use one can boost your confidence during emergencies.
CPR for Infants and Children
Responding to an emergency involving a child or infant requires different techniques. Online courses teach how to modify compressions and breaths for younger patients. For example, infant CPR uses two fingers instead of both hands, and the depth of compressions is shallower. These distinctions are essential for ensuring safe and effective care.
Dealing with Choking Emergencies
Choking is another common life-threatening emergency, especially in children. Online CPR courses often include lessons on how to perform abdominal thrusts (commonly known as the Heimlich maneuver) for both adults and children. You’ll also learn how to clear the airway for infants by delivering back slaps and chest thrusts.
Final Thought
The goal of online CPR courses is not just to teach techniques but to build your confidence in applying them. Many programs offer video demonstrations, quizzes, and virtual simulations to reinforce learning. Some even encourage follow-up hands-on practice with a local instructor to ensure you’re fully prepared for real-life situations.