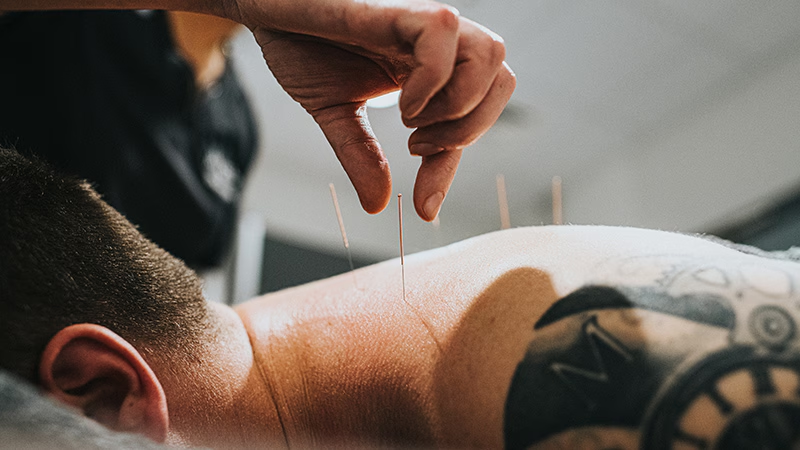
Acupuncture has gained attention among researchers and patients as a popular method for promoting healing and pain relief. Practices at a Chinese Acupuncture Center are rooted in ancient Chinese medicine and are increasingly backed by scientific studies aiming to explain how acupuncture works. This article explores the scientific mechanisms behind acupuncture, how it interacts with the body, and why it continues to be a trusted therapy worldwide.
Understanding the Basics of Acupuncture
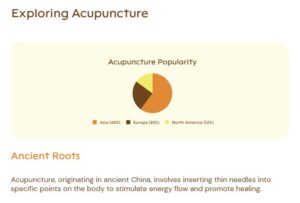
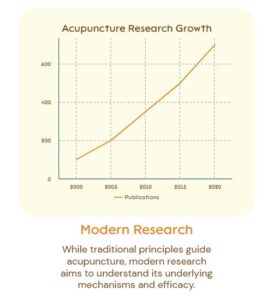
Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to restore balance and encourage healing. Traditionally, Chinese medicine views acupuncture as a way to balance Qi (or “chi”), the body’s vital energy. By stimulating acupuncture points, practitioners believe they can correct imbalances in the body’s flow of energy, which can alleviate pain and other symptoms.
In Western medicine, the process is examined from a scientific perspective, looking at physical responses to needle insertion rather than energy channels. This shift provides a framework for investigating acupuncture in terms of neurochemical and physiological changes, helping to clarify why it can be effective for various health concerns.
How Acupuncture Interacts with the Nervous System
One of the primary scientific explanations for acupuncture’s effectiveness is its interaction with the nervous system. The process of needle insertion at specific points stimulates nerve endings in the skin and underlying tissues, which can result in:
- Activation of the Brain and Spinal Cord: Needle insertion triggers a response from the brain and spinal cord, leading to the release of neurotransmitters, such as endorphins and enkephalins, that are known for pain relief.
- Pain Modulation: This neurological stimulation helps inhibit pain signals from reaching the brain, reducing the perception of pain. For chronic pain sufferers, acupuncture offers a potential alternative to medication for managing discomfort.
- Improved Blood Flow and Circulation: Acupuncture points often coincide with major blood vessels, which can improve local circulation when stimulated. Enhanced blood flow can aid healing by delivering more oxygen and nutrients to injured or inflamed areas.
The Role of Neurotransmitters and Hormones in Acupuncture
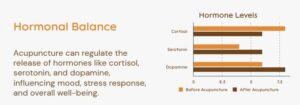
Acupuncture has been shown to influence the body’s production of specific neurotransmitters and hormones, which helps explain its ability to relieve stress, reduce inflammation, and improve overall well-being. Some of these key compounds include:
- Endorphins: Known as natural painkillers, endorphins are released during acupuncture treatment, which helps reduce pain levels and elevate mood.
- Serotonin and Dopamine: These “feel-good” neurotransmitters are also affected by acupuncture. Many patients report feeling relaxed and less stressed after treatment, likely due to increased serotonin and dopamine levels.
- Cortisol: Acupuncture can help reduce levels of cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, which can lead to a more relaxed state. Lower cortisol levels have also been linked to improved immune function, better sleep, and a reduction in anxiety.
How Acupuncture Affects Inflammation and the Immune System
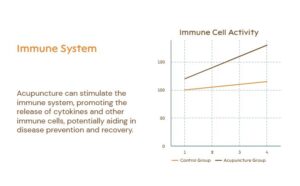
Recent studies indicate that acupuncture can help modulate the body’s immune response, which is beneficial for treating inflammatory conditions and supporting general health. Inflammation, a common response to injury or infection, is reduced as acupuncture stimulates natural anti-inflammatory pathways.
By modulating the production of specific proteins and cytokines, acupuncture helps control inflammatory processes within the body. This response is particularly valuable for those suffering from autoimmune disorders, arthritis, and chronic inflammatory conditions, as it provides a non-invasive approach to managing inflammation.
Key Benefits of Acupuncture’s Impact on Inflammation
- Reduced Swelling: Acupuncture can decrease localized swelling, making it beneficial for injuries and inflammatory conditions.
- Enhanced Recovery: Improved blood flow to affected areas supports tissue repair and recovery.
- Immune Support: By balancing immune responses, acupuncture aids in defending against illness and supporting long-term health.
The Gate Control Theory: Blocking Pain Signals
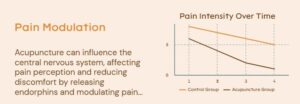
The Gate Control Theory offers another scientific rationale for acupuncture’s effectiveness in pain management. According to this theory, pain signals must pass through neural “gates” in the spinal cord before reaching the brain. Acupuncture helps to “close” these gates, thereby blocking or reducing the intensity of pain signals.
When a needle is inserted, it stimulates nerves in the affected area, which triggers inhibitory nerve pathways that prevent pain signals from reaching the brain. This explains why acupuncture is widely used for chronic pain management, including conditions like back pain, migraines, and arthritis.
Acupuncture and the Endocannabinoid System
In addition to the nervous system and neurotransmitters, acupuncture may also influence the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a crucial role in regulating pain, mood, and immune responses. The ECS consists of cannabinoid receptors found throughout the body that help maintain balance or homeostasis.
Research suggests that acupuncture can activate the ECS, leading to increased production of endocannabinoids, which have natural pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory effects. This finding provides further evidence for acupuncture’s role in promoting relaxation, enhancing mood, and reducing discomfort.
Benefits of Acupuncture’s Influence on the Endocannabinoid System
- Natural Pain Relief: By stimulating endocannabinoid production, acupuncture can offer pain relief without medication.
- Mood Regulation: Activation of the ECS helps alleviate stress and anxiety, contributing to a greater sense of well-being.
- Reduced Inflammation: The ECS response promotes anti-inflammatory effects, supporting joint health and immune function.
Conclusion:
Acupuncture’s scientific basis lies in its ability to influence the nervous system, regulate neurotransmitters, modulate immune responses, and activate the endocannabinoid system. These mechanisms work together to offer pain relief, reduce inflammation, and support mental well-being. Whether you’re seeking an alternative therapy for pain or looking for holistic health support, acupuncture provides a scientifically backed approach to wellness. For those interested in experiencing the benefits of this therapy, finding a Chinese Acupuncture Center nearby can be an excellent place to start exploring its therapeutic effects.